
Lately, I’ve been talking about transmedia storytelling to whoever will listen. If you’re not familiar with this approach, transmedia refers to a story that is told on multiple media platforms, with different parts of the story appearing in different places. The readers/viewers may enter the story at various points, and may need to solve puzzles or follow clues to discover the different nodes of the story. Transmedia is different from multimedia, which would be a retelling of the same story told using different media (e.g., a movie, a graphic novel, an audiobook). Beyond using transmedia for the sheer joy of telling a story, this approach is now often used to promote television shows and movies, as well as marketing products. Want to try out a quick example of a transmedia story in action? No Mimes Media has created a 10-minute alternate reality game (ARG) you can experience online. (Hint: Look for clues to get to each of the next parts of the story and keep your phone nearby.)
Why Use Transmedia in Social Marketing?
For all the reasons that the entertainment education approach works to change knowledge, attitudes and behaviors, transmedia storytelling has the potential to match and exceed that success. Entertainment education-based social marketing has traditionally focused on “product placement” of health and social issues within the plotlines of television shows, radio serials, movies, video games and other individual media. When someone is wrapped up in the plotline of a show and their favorite character becomes sick or models a positive behavior, that person is more likely to remember information delivered in the course of the program and desire to act on it.
In a transmedia story, you are immersed in the plotline either as the main character or as you get to know the characters and their world from many different angles. Often, transmedia stories are told in real-time, with the characters posting to their Twitter accounts, writing blog posts and creating YouTube videos. They may come to feel like friends, especially if the audience is encouraged to interact with the characters. This type of immersive experience can make a strong impression on knowledge, attitudes and perceptions of social norms, and can motivate action.
What Might Have Been
Transmedia is one of those things more easily understood with a tangible example, so I spent some time thinking about how I might structure a campaign. I remembered that a couple of years ago, as part of the Great California ShakeOut (a statewide earthquake drill), the event included a simulation game called After Shock that did not quite live up to its great potential. The idea was that during and after the earthquake drill, participants would use blogs, Twitter, video, photos and more to document what happened to them personally during the “earthquake” and how they were dealing with the aftermath. It was a fun, exciting idea, and I played along, startling my Twitter friends and posting to the blog on my account at the site. Many others did as well, with blog posts, photos of “earthquake rubble,” and other creative stories that showed they had thought through the implications of how an earthquake would impact their lives. Unfortunately, there was not much direction from the coordinators as to what we were supposed to do, and participation fizzled. (At least from my viewpoint, I didn’t see much happening on the site and did not receive any clear instructions to help me continue.)
What’s Shakin’? Earthquake Preparedness Transmedia Campaign
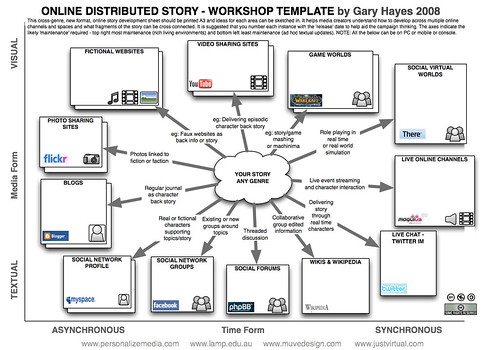
I’ve put together a sample transmedia campaign that addresses the flaws of what After Shock could have been, with the goal of motivating earthquake preparedness in Southern California. I was inspired by Gary Hayes’ transmedia worksheet (below) and the creativity of Luci Temple’s hypothetical transmedia case study based on the television show “V.”
Objectives
What’s a campaign without objectives? Here are the main ones I’d be shooting for:
- To increase the number of people who know what to do to prepare for an earthquake.
- To increase the number of people who know what to do during and immediately after an earthquake.
- To increase the number of people who believe that being prepared is important and doable.
- To increase the number of people who create a family emergency plan.
- To increase the number of people who have an earthquake/emergency kit in their homes, offices and cars.
- To increase the number of people who take preventive measures to secure their homes to prevent damage during an earthquake.
Narrative
In transmedia storytelling, the story narrative is often in the background or not visible at all. Designers must write the backstory and timeline, and then identify the “artifacts” (tweets, postcards, YouTube videos, etc.) that the characters create as a result of that story. It’s often up to the participants to piece together exactly what happened, and where they might need to read between the lines.
Here’s the basic narrative of a possible storyline (yes, it’s kind of silly), and afterward we’ll look at how the transmedia campaign could bring it into being:
Shaky McShakerson works in downtown LA as an IT guy in the City’s Bureau of Important Processes. He’s married to Terra McShakerson, who works out of their house in Sherman Oaks as a photographer specializing in doggie fashion. They have two kids – Tembla (4) and Shaker Jr (1).
10:36 am Tuesday morning, a 7.7 earthquake hits LA, centered in Hollywood. Shaky’s at work – he has to help out with the city’s response. Terra is at a doggie fashion shoot in Pasadena. Tembla is at preschool and Shaker Jr. is with Terra’s mother in Van Nuys.
Shaky and Terra can’t connect with each other via phone. They had no plan for emergencies and have no idea what condition their home is in. The immediate aftermath of the earthquake is chaos: a 405 freeway overpass is down, traffic lights are out across the city, they can see smoke from several locations in the distance. Finally they are able to connect with each other via Twitter, but Terra still can’t reach her mom or the preschool.
Shaky is part of the emergency response and is responsible for setting up a blog to keep people informed through official channels. He can’t leave his post downtown, so Terra is on her own.
Terra jumps in the car and tries to move as quickly as she can from Pasadena to Van Nuys. She runs into many roadblocks along the way. Finally she arrives at her mother’s house, which is intact, although several houses on the street have collapsed chimneys and broken windows. She sees that her mother and Shaker Jr are fine, but she needs to get to Tembla. She arrives at the preschool and sees that it is in shambles. Everyone has been evacuated and parents are freaking out looking for their kids. Finally someone remembers to call the emergency out of state phone number that was given at the beginning of the year and they find out that the teachers brought the kids to the elementary school yard down the street. She collects Tembla, who is very upset and traumatized.
She takes the children back home, and discovers that their house did not fare very well. Gas is leaking, and it takes a long time for her to find a wrench and the shut-off valve. The house is full of broken glass, the floor is covered with what had been on the shelves, and the furniture has traveled across the rooms. The electricity is out, and the water does not seem to be working either. Terra sets to work trying to figure out what she needs to do now and how to begin to recover.
The days and weeks that follow include some major aftershocks, anxiety attacks from Tembla, and the realization that they should have been much more prepared. They don’t have enough food, water and medical supplies. The city is not recovering very quickly. The survivalist neighbors who they always thought were crazy for storing months worth of food are the only ones on the block who are doing well. Terra’s best friend Florence is a nurse and shares stories of what she’s seen in the hospital.
Terra and Shaky decide to get prepared for the next disaster and put together their supplies. So when a 6.1 aftershock hits, they are ready and able to deal with it, and get on with their lives without much hassle.
The Transmedia Campaign
1) Billboards will be posted around the city for “Terra’s Doggie Fashion Fotos” including the URL (ads will be so ridiculous that people look for the website to see if it’s a joke). Also, street teams passing out postcards with the same image/URL at gathering places around LA.
2) A website for Terra’s business will include her phone number (with voice mail message) and links to her Facebook page and Twitter account. The text will use earthquake metaphors as clues for what the campaign is about and provide insight into her personality and lifestyle.
3) Terra’s Twitter account will be the main driver of the narrative (with tweets also going to her Facebook page), and here is where we will also meet Shaky and Florence via their accounts. Quite a bit of interaction will have already occurred before the campaign begins. When the earthquake hits, we can see Terra’s panicked response and her attempts to reach her family. She and Shaky reach each other via Twitter. She urges people to call her on her cell if they know anything about her mom and kids.
4) When people call her cell phone number, they’ll hear her message about what she’s seeing on the streets as she’s trying to get to her family and her relief as she arrives at her mother’s house. She uses Twitpic to post pictures of the damage she sees all around.
5) Meanwhile, Shaky is setting up a blog for his city department that provides updates on what’s happening around the city in terms of emergency response, as well as safety information. He invites people to post comments about what happened to them during the earthquake and whether they were prepared. He shares the “official” department website and phone hotline that people can call over the next week for updates.
6) Once back at home, Terra tweets about the challenges they are facing and looks for information on what to do to prevent any further damage. She finds a smartphone app and companion website (created by the campaign) with earthquake preparedness information and shares that information on Twitter.
7) Over the next week, Terra uses Twitter to give updates on what she’s doing to prepare for the next earthquake, and uploads some video to YouTube. She posts information about caring for pets in earthquakes on her business Facebook page. Shaky uses the blog to give tips on preparedness and to invite participants to a live event.
8) The campaign concludes with a live event coinciding with the Great California Shakeout, where Terra and Shaky make an appearance to urge earthquake preparedness (and to take doggy fashion fotos). Those with smartphones will be able to see a simulated aftershock in real time via augmented reality, to reinforce how to respond.
There are many more touchpoints we could add (e.g., TV, radio, live chat, etc.) but this gives you a flavor of how it might all work together. Of course, keep in mind that this approach can only work if members of your target audience are already using most or all of these media. You would need to do research with them to find out what media they use, and what their current knowledge, attitudes and behaviors are, before jumping into creating the campaign.
Any takers?
Some Transmedia Resources (Updated 6/30/10)
- Transmedia, Hollywood: S/Telling the Story – panels from conference held at USC
- TranSocialMedia Storytelling & ARG Workshop Sheet – useful worksheet from Gary Hayes
- Transmedia Project “Bible” Template (.docx) – strategic planning template from Robert Pratten of Zen Films
- Transmedia Activism: Telling Your Story Across Media Platforms to Create Effective Social Change – article by Lina Srivastava (and Lina’s website transmedia-activism.com)
Photo: chiaralily

 Nedra helps nonprofits and public agencies create positive change on health and social issues through social marketing and transmedia storytelling strategies at Weinreich Communications since founding the company in 1995. She helps organizations make a difference for the populations they serve by strategically designing programs that draw on state-of-the-art behavior change techniques, digital media approaches and the power of stories.
Nedra helps nonprofits and public agencies create positive change on health and social issues through social marketing and transmedia storytelling strategies at Weinreich Communications since founding the company in 1995. She helps organizations make a difference for the populations they serve by strategically designing programs that draw on state-of-the-art behavior change techniques, digital media approaches and the power of stories. 
Trackbacks/Pingbacks